“Exercise is Medicine” (EIM) ranked sixth among the top global fitness trends for 2020 in the American College of Sports Medicine’s (ACSM) annual survey of fitness professionals, up from #10 in 2019. EIM ranked third in Asia, sixth in North America, and eighth in Europe.
Similarly, fitness programs aimed at improving health for older adults ranked eighth overall among the top global fitness trends; exercise for weight loss 11th. Lifestyle medicine (e.g., exercising to improve sleep or energy) and exercise for children are new to the top 10 trends for 2020, per ACSM.
In Asia and South America, exercise for weight loss ranks first among the top 2020 fitness trends. Exercise as lifestyle medicine ranks second in South America; exercise for children/teens ranks second in Asia. Fitness for older adults is among the top 10 trends in North and South America.
Perhaps most exciting is ACSM’s global Exercise is Medicine health initiative, which encourages physicians/healthcare providers to include physical activity when designing treatment plans and to include EIM Credentialed Exercise Professionals as part of the healthcare team.
In 2019, the Global Wellness Institute reported that doctors in the U.K. and Singapore were prescribing exercise with public support and infrastructure to implement their recommendations.
Figure 1. Top 20 Worldwide Fitness Trends for 2020

Source: American College of Sports Medicine, Worldwide Survey of Fitness Trends for 2020 (Thompson, Walter R. ACSM’s Health & Fitness Journal 23(6):10-18, November/December 2019. doi: 10.1249/FIT.0000000000000526 Included but not limited to professionals in Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, Japan, India, Italy, Russia, Singapore, Spain, Taiwan, U.K., and U.S.)
COVID as Catalyst
COVID-19 has been a unique catalyst for the “exercise as medicine” movement, reflecting an unprecedented global consumer desire to take control of one’s own personal health.
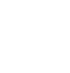
According to HealthFocus’ November 2020 Global COVID-19 report, over one-third of global consumers surveyed now agree that their short-term health depends on how well they take care of themselves. Nearly half (46%) reported they are now in greater control of their health, 36% are eating a healthier diet, and 28% are more active (Figure 2).
Personal health/physical well-being is now also the number one source of happiness worldwide, per IPSOS Global Happiness Survey (fielded Jul./Aug. 2020 in 26 major global markets).
In fact, the self-care trend is so strong that Euromonitor added the Self-care Aficionado in 2020 as one of 12 global consumer types/segmentations in its annual Lifestyle Survey. Self-care consumers, focused on their physical/mental well-being, represent 5% of the global adult population.
In August 2020, eight in 10 (79%) of U.S. consumers said that taking care of their health was a top priority. Half (48%) said they will purchase more items related to health/nutrition, per ADM’s proprietary OutsideVoice. Seven in 10 (72%) think it is important to have an active lifestyle, per Mintel’s August Global Trend Wellbeing report.
“Fit consumers,” who live a healthy active lifestyle differentiated by integrating frequent physical exercise (three to five days/week) and a focus on enhancing everyday mental and physical health are most likely to further embrace the “exercise as medicine” movement. In August 2020, Mintel estimated this group of everyday exercisers who take a more holistic approach to health at 37% of U.S. adults, in contrast to 16% who consider themselves athletes.
(FOR MORE ANALYSIS ON 'THE FIT CONSUMER, VISIT THIS TRENDSENSE ARTICLE.)
Figure 2. Global COVID Directed Lifestyle Changes
Source: HealthFocus’ 2020 Global COVID-19 Report
Exercise as Remedy (Rx Exercise)
In recent years in the U.S., exercise has become an increasingly popular and often preferential tool in helping to treat or prevent adverse health conditions, according to the Hartman Group’s Health + Wellness 2019: From Moderation to Mindfulness Report.
In 2019, Hartman reported over half of U.S. adults were actively dealing with one or more chronic health conditions in their household. On average, consumers were treating 3.5 conditions while trying to prevent 6.1.
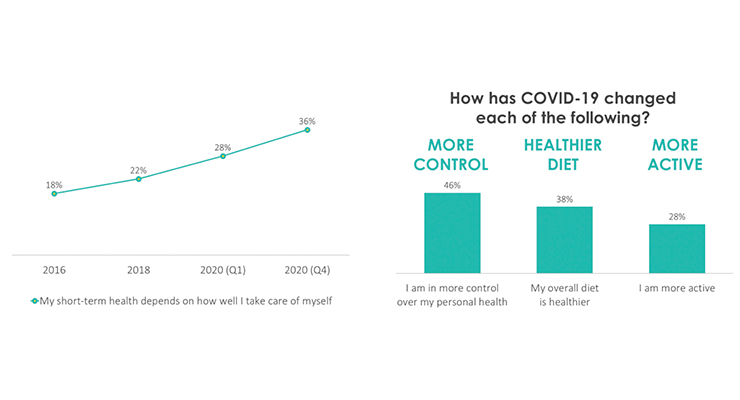
Weight loss topped the list of conditions consumers were trying to treat/prevent with exercise, followed by anxiety/stress, fatigue, heart/cardio concerns, diabetes, and memory/cognitive decline (Figure 3).
Most important is that the conditions Americans were most likely to treat with exercise last year are among those where concern has accelerated since the pandemic.
Figure 3. Exercise as Remedy for Health Condition
Source: Hartman Group’s Health + Wellness 2019: From Moderation to Mindfulness Report
Anxiety/stress was the top condition two-thirds of U.S. consumers tried to manage/prevent last year, per the Hartman survey. In August, Mintel’s US COVID-19 Tracker reported that nearly two-thirds of U.S. consumers were actively seeking ways to reduce stress. Two-thirds struggled to fall asleep, 42% had made mental well-being a higher priority. In February, Euromonitor’s Health & Nutrition survey reported that half (51%) of global consumers were moderately/extremely concerned about stress/anxiety.
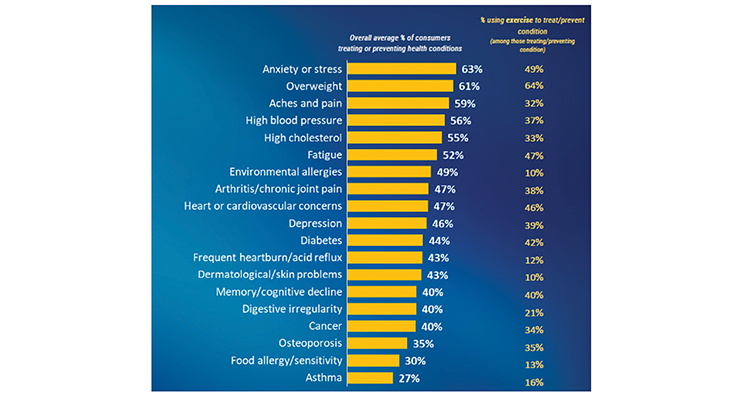
Four in 10 U.S. Gen Z adults aged 18-24, one-third of Millennials and Gen X, and just over one-quarter of Boomers reported gaining weight since the COVID-19 pandemic began, according to the October “State of Fitness & Sports Nutrition During Covid” webinar presentation (Figure 4).
Figure 4. COVID-19 Acclerates Concern Over Specific Health Condistions
Source: Natural Marketing Institute, 2020
According to Euromonitor’s October 2020 In Search of a Healthy Lifestyle, globally, 57% of Millennials are trying to lose weight. Exercise is the second most popular weight loss method worldwide after drinking more water, per Euromonitor.
With the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in August confirming that those with pre-existing serious heart conditions—including coronary artery disease and hypertension—are at an increased risk of severe illness from COVID-19, there is an even greater incentive to more aggressively manage, monitor, and treat cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Nearly half of U.S. adults have some form of CVD; 116 million high blood pressure, and 93 million cholesterol levels greater than 200 mg/dL, according to the American Heart Association’s 2020 statistics. Globally, 233 million adults have CVD; 39% high cholesterol, and 26% high blood pressure, per the World health Organization’s (WHO) 2019 statistics.
(FOR MORE INSIGHT ON HOW COVID HAS REFOCUSED ATTENTION ON HEART HEALTH, VISIT THIS TRENDSENSE ARTICLE.)
Concern over diabetes, also a significant risk factor for COVID-19, has risen since the pandemic. The American Diabetes Association reported 26.8 million U.S. adults were diagnosed with diabetes in 2018; 92 million had metabolic syndrome. On average, there are 1.5 million new cases of diabetes per year in the U.S. Globally, 463 million adults (age 20-79) were living with diabetes in 2019, per the International Diabetes Federation; 60% of diabetics live in Asia.
Global immunity seekers are much more likely than the general population to cite fitness/endurance as a top attribute for being healthy, per Euromonitor. Although immunity seekers have traditionally skewed younger (aged 25-44 with children at home), since COVID those aged 60 and older in the U.S. and China now top the list.
Half of gym goers/health club members are concerned about their immunity (61% Boomers, 49% Gen X, 36% Millennials, 37% Gen Z), per the International Health, Racquet & Sportsclub Association’s (IHRSA).
Growth in Exercise as Medicine
The “exercise as medicine” movement is poised for substantial growth and, just as the “fit consumer” trend, will likely further redirect the sports nutrition market toward mainstream active consumers.
In August, Mintel’s COVID-19 Tracker reported that more than one-third of consumers made exercise a higher priority. Over half (57%) surveyed by ADM for its October Sports Nutrition for the Game of Life webinar, said they planned on exercising even more in the remainder of 2020 and in 2021.
Health was already the top reason to exercise for 75% of U.S. consumers in 2019, followed by managing weight 61%, building strength 47%, living longer 46%, improving mood 41%, endurance 41%, building muscle 36%, aerobic fitness 28%, and disease prevention 22%, per HealthFocus’ 2019 USA Consumer Survey (Figure 5).
Figure 5. Reasons to Exercise
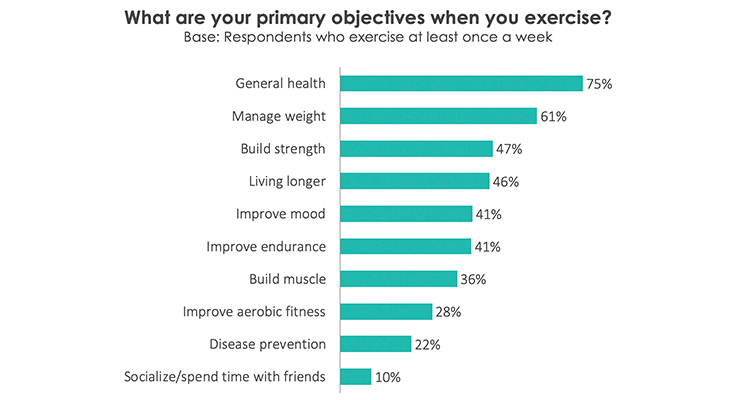
Source: HealthFocus, 2019 USA Consumer Survey
Six in 10 (58%) of all fitness club/gym members surveyed by IHRSA in October 2020 said they’re more committed to being physically active, eating healthier (57%), and taking better care of their mental health (42%) than ever before. Three in four gym goers said they’re feeling anxious about their health.
Those at risk of severe complications from COVID-19 and older consumers are also somewhat more committed to being more physically active than those who have fewer comorbidities (60% vs. 56%), per IHRSA. Electronic health monitoring devices will play an important role in the EIM movement.
Gym closures and the move to at-home and solo exercising have also created a series of new and often virtual product opportunities. Prior to the pandemic, Mintel reported that over half of exercisers in the U.S. were already working out in their home.
Going forward, 63% surveyed by IHRSA said they’d prefer a mix of going to the gym and working out at home. In 2019, 73.6 million Americans were health/fitness club users; revenues topped $34.5 billion, per IHRHA.
Prior to the pandemic, 42% of gym goers went three to four days a week. As gyms reopen, almost as many (35%) have anticipated they’d be going just as often—and nearly all (94%) said they’ll return in some capacity, per IHRSA.
For most consumers, exercise intensity has been moderate; 63% said low impact workouts are their preferred method, per Mintel’s August Exercise Trends – US update.
According to the National Sporting Goods Association Sports Participation Study of April 2020, walking is the largest sports activity (Figure 6). Of note, NSGA reported that female participation of all ages is on the rise in 40 of 57 sport activities. Overall, fitness activities posted the highest gains in 2019.
Figure 6. Sport/Recreational Activity Participation 2019
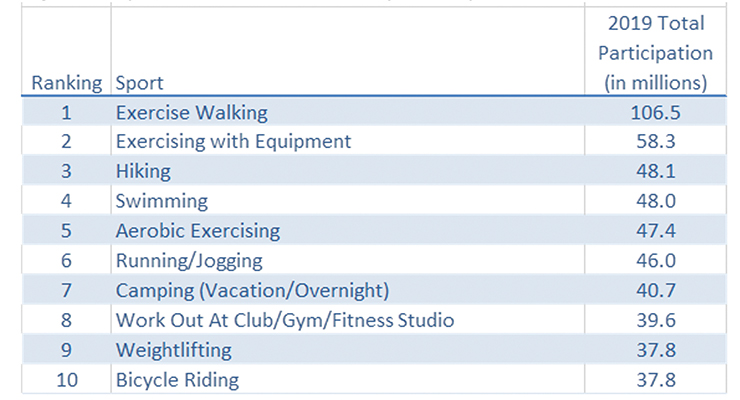
Source: National Sporting Goods Association Sports Participation Study, April 2020
Figure 7. Participation in Millions by Gender in 2019 for the Six Fitness Activities Listed in Figure 6
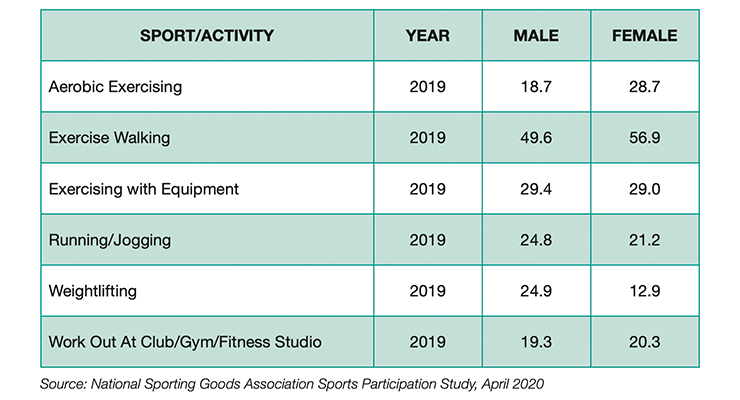
In June 2020, Nutrition Business Journal reported that 24% of consumers were doing more walking/hiking than the same time frame a year ago; 15% more online or at-home exercise videos, 14% running, 9% yoga, and 7% each biking and weightlifting.
A New Generation of Exercise Aids
Perhaps most exciting is the ability to better tailor product forms, messages, and multi-functional solutions to the new movement’s needs (e.g., performance products with immune boosting properties for active adults who are trying to treat/prevent specific conditions or lifestyle issues).
For example, when trying to treat/prevent anxiety/stress, half (49%) of U.S. consumers most often chose exercise as a solution, followed by OTC/Rx medication (32%), food/beverage 20%, supplements (16%), and alternative care 14%, per the Hartman Group. For weight management, exercise is the remedy of choice (64%), followed by food/beverage (61%) and supplements (14%). For memory/cognitive decline, supplements are second only to exercise (40% vs. 30%). OTC/Rx solutions are opted for most frequently for aches/pains followed by exercise (65% vs. 32%), per Hartman.
In 2019, one-third (36%) of consumers always/usually had a food/beverage before exercising, 26% during, and 48% after, per HealthFocus 2019 USA Study. Moreover, 29% of adults said they always/usually changed what they ate to meet their body’s needs for different levels of activity. According to Hartman’s Functional Food and Beverage and Supplements from April 2020, hydration is the number one functional benefit exercisers are interested in.
CRN’s COVID-19 Survey (October 2020 supplement survey) found that one-third (43%) of those who had increased their supplement use during the pandemic increased their use of sports nutrition supplements, 14% used protein (powders, drinks, and bars) and 13% energy drinks/gels; CRN’s fall survey showed a slight dip in use. In the fall of 2020, 30% of users took a sports supplement vs. 36% in 2019. One in five users reported taking protein, 10% energy drinks, and 5% amino acids.
New and innovative ingredients should grab the attention of Gen X and Millennial exercisers; they are the most frequent exercisers and the desire for new and cutting edge ingredients skews younger. These demographics will show interest in new performance enhancing properties of familiar ingredients (e.g., probiotics and prebiotics), and performance-related potential for new ingredients like postbiotics.
Nearly half (45%) of active parents/gym goers are worried about their child’s health, 42% their mental health; and they are actively encouraging their children to exercise, per IHTSA. Nearly half of global fitness-focused parents said their children rarely eat snacks between meals, seek natural and organic foods, avoid artificial sweeteners, and look for ingredients promoting heart and digestive health for their kids, per Euromonitor.
Lastly, sports nutrition and weight loss products have been among the temporary causalities of the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly driven by health club and gym closures, which limited the use of sports nutrition products by its regular consumer base. Moreover, some will remain skeptical about returning to old forms of exercising.
In March 2020, Nutrition Business Journal projected the sports nutrition and weight management industry would grow from $45 billion in 2019 to over $50 billion in 2022. On a global scale, Euromonitor expects both categories to bounce back over the next few years (Figure 8).
Figure 8. Coronavirus Accelerates Demand for Immunity and Holistic Wellness
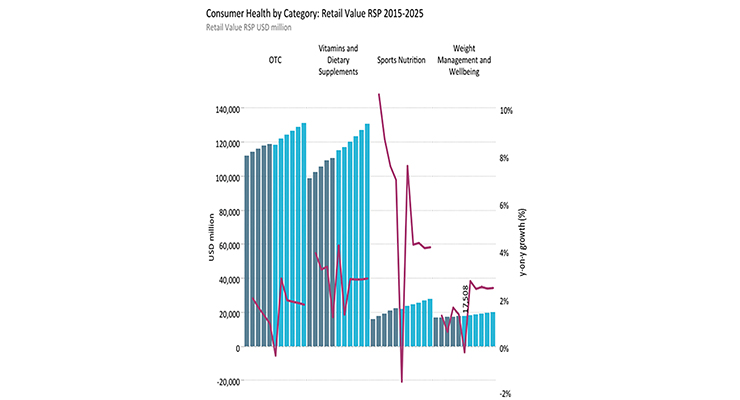
Source: Euromonitor International Blog Oct. 26, 2020
Dr. A. Elizabeth Sloan & Dr. Catherine Adams Hutt
Sloan Trends, Inc.
Dr. A. Elizabeth Sloan and Dr. Catherine Adams Hutt are president and chief scientific and regulatory officer, respectively, of Sloan Trends, Inc., Escondido, CA, a 20-year-old consulting firm that offers trend interpretation/predictions; identifies emerging high potential opportunities; and provides strategic counsel on issues and regulatory claims guidance for food/beverage, supplement and pharmaceutical marketers. For more information: E-mail: lizsloan@sloantrend.com; Website: www.sloantrend.com.