10.25.19
According to a survey of 200 U.S.-based registered dietitian nutritionists (RDNs), 66% of RDNs said they recommend both food and dietary supplements to their clients; 70% personally take supplements four times or more per week. The data came from Trust Transparency Center's 2019 Registered Dietitian Insights Survey.
Dietitian Personal Supplement Usage
The top 10 supplements dietitians reported they personally used were:
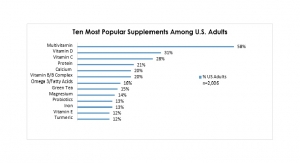
1. Multivitamins/multivitamin injections (50%)
2. Vitamin D (43%)
3. Fish Oil/Omega/Krill (26%)
4. Calcium (25%)
5. Probiotics (17%)
6. Vitamin C (10%)
7. Protein (8%)
8. Biotin (8%)
9. Minerals (7%)
10. B Complex (6%)
These dietitians primarily rely on their own research when deciding to take supplements, with dietary deficiencies being the biggest concern (52%), followed by personal research (49%) and personal physician recommendation (31%). Other reasons for taking supplements include condition-specific concerns such as inflammation, energy, GI issues, etc.
Dietitian Education & Knowledge of Supplements
Most dietitians surveyed were formally educated on the use of supplements, generally while obtaining their nutrition degree (73%) followed through by continuing education (60%). They stay informed regarding supplements via continuing education, medical journals, and colleagues.
Regarding nutritional ingredients, the supplementation conversation may need to extend to functional foods in order to appeal to dietitians that prefer food solutions.
Supplement Recommendations to Patients & Clients
Over three quarters of dietitians recommend supplements to 25% or more of their clients, and dietitians who use more supplements themselves are more likely to recommend them to their patients. The most popular reasons for making recommendations include dietary deficiencies, poor nutrition, caloric needs, wound care, GI or renal problems, and old age. The top five supplements they recommend are:
Dietitians are also increasing their recommendations for specialty supplements such as prebiotics, CoQ10, curcumin/turmeric and collagen. These recommendations are being driven by an increase in research in these categories and dietitians being better informed.
"Americans are generally failing with their diets and physicians have self-reported they're not equipped to address dietary concerns. Dietitians are the optimal conduit to educating people on nutritional needs and supplements have a clear place as part of other healthy lifestyle changes," said Traci Kantowski, certified health coach and Trust Transparency Center's communications director. "This research shows that dietitians are taking supplements themselves and recommending them, but will benefit from more education."
TTC conducts this dietitian survey and other insight research on an annual basis.
TTC will be sharing these insights and other information on behalf of the Global Prebiotic Association, Global Curcumin Association and the Coconut Coalition of the Americas at Booth #964 at the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (AND) Food and Nutrition Conference and Expo (FNCE) in Philadelphia Oct. 27 to 29.
Dietitian Personal Supplement Usage
The top 10 supplements dietitians reported they personally used were:
1. Multivitamins/multivitamin injections (50%)
2. Vitamin D (43%)
3. Fish Oil/Omega/Krill (26%)
4. Calcium (25%)
5. Probiotics (17%)
6. Vitamin C (10%)
7. Protein (8%)
8. Biotin (8%)
9. Minerals (7%)
10. B Complex (6%)
These dietitians primarily rely on their own research when deciding to take supplements, with dietary deficiencies being the biggest concern (52%), followed by personal research (49%) and personal physician recommendation (31%). Other reasons for taking supplements include condition-specific concerns such as inflammation, energy, GI issues, etc.
Dietitian Education & Knowledge of Supplements
Most dietitians surveyed were formally educated on the use of supplements, generally while obtaining their nutrition degree (73%) followed through by continuing education (60%). They stay informed regarding supplements via continuing education, medical journals, and colleagues.
Regarding nutritional ingredients, the supplementation conversation may need to extend to functional foods in order to appeal to dietitians that prefer food solutions.
Supplement Recommendations to Patients & Clients
Over three quarters of dietitians recommend supplements to 25% or more of their clients, and dietitians who use more supplements themselves are more likely to recommend them to their patients. The most popular reasons for making recommendations include dietary deficiencies, poor nutrition, caloric needs, wound care, GI or renal problems, and old age. The top five supplements they recommend are:
- Multivitamin (and multivitamin injection) (50%)
- Vitamin D (40%)
- Calcium (27%)
- Probiotics (20%)
- Protein (18%)
Dietitians are also increasing their recommendations for specialty supplements such as prebiotics, CoQ10, curcumin/turmeric and collagen. These recommendations are being driven by an increase in research in these categories and dietitians being better informed.
"Americans are generally failing with their diets and physicians have self-reported they're not equipped to address dietary concerns. Dietitians are the optimal conduit to educating people on nutritional needs and supplements have a clear place as part of other healthy lifestyle changes," said Traci Kantowski, certified health coach and Trust Transparency Center's communications director. "This research shows that dietitians are taking supplements themselves and recommending them, but will benefit from more education."
TTC conducts this dietitian survey and other insight research on an annual basis.
TTC will be sharing these insights and other information on behalf of the Global Prebiotic Association, Global Curcumin Association and the Coconut Coalition of the Americas at Booth #964 at the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (AND) Food and Nutrition Conference and Expo (FNCE) in Philadelphia Oct. 27 to 29.