By Dr. A. Elizabeth Sloan & Dr. Catherine Adams Hutt, Sloan Trends, Inc.05.02.19
Helping to prevent/treat digestive issues has spawned one of the largest and fastest growing supplement, functional food/beverage, and OTC markets in recent years. Eight in 10 U.S. adults suffer annually from a digestive issue, 37% regularly and one in five daily, per Mintel’s 2018 Digestive Health U.S. - July. Those aged 18-34 are the most likely to be afflicted.
Gastrointestinal supplement sales reached $2.96 billion in 2018 and are projected by Nutrition Business Journal (NBJ) to reach $3.98 billion by 2021.
One in five U.S. supplement users took a digestive supplement in 2018; probiotics were the 8th most often used supplement, taken by 17% of all users. One in five (20%) young adults aged 18-34 used a fiber supplement, 16% a probiotic, 7% digestive enzymes, and 5% prebiotics, per CRN’s 2018 Consumer Survey on Dietary Supplements.
Over one-quarter (28%) of adults cite digestive health among the top three benefits they want from foods/beverages, per IFIC’s 2018 Food & Health Survey; two-thirds of those age 50 and over say digestive health is extremely/very important. Four in 10 adults (43%) are trying to get more probiotics in their diet, per Hartman’s Wellness 2017.
OTC digestive remedies, including antacids, laxatives, anti-gas, and anti-diarrhea reached $4.9 billion in 2018, up 11.9% over the past five years, per Mintel.
Yet it’s the mounting medical evidence, and growing consumer awareness, that a healthy gut microbiome can deliver a wealth of high-demand and often difficult-to-achieve health benefits, (e.g., improved mood and better memory) that is poised to drive explosive growth in the digestive market—and the timing is now!
Microbiome Moves Center Stage
According to HealthFocus’ 2019 U.S. Consumer Trends Survey, over one-third (37%) of U.S. consumers are aware of and extremely/very interested in the gut microbiome, and how good and bad bacteria in the gut impact overall health. Young adults aged 18-39 and those in households with kids are most interested.
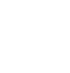
Two-thirds of those who take a probiotic supplement do so for a healthier microbiome/gut, 49% general well-being, 45% regularity, 43% immunity, 34% to replenish good bacteria after antibiotic use, and 32% for better nutrient absorption, per Mintel’s February 2019 Gut Health is Today’s Hot Health Issue report (Figure 1).
Figure 1

Source: Mintel, 2019
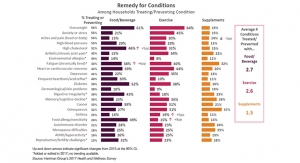
Most important, 64% of consumers believe their digestive health plays an extremely/very important role in their physical health, 58% weight management, 57% daily energy levels, 56% overall mental well-being, 55% immune function, 54% aging well, 51% mood/stress levels, and 48% physical appearance, per HealthFocus (Figure 2).
A significant body of scientific evidence supports a connection via the gut-brain axis for improved cognitive health, mood, reduced stress, and potentially neurodegenerative conditions (e.g., Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease).
In a 2017 NBJ survey, nutraceutical manufacturers cited brain health as the top opportunity for the next few years. In 2018, CRN reported that 26% of users bought a supplement for mental/brain health. Brain/cognitive supplements sales are projected to exceed $1 billion by 2021, per NBJ; mental health/mood and anti-stress supplements reached $706 million in 2018.
Figure 2
Source: HealthFocus, 2019
Maintaining brain function with age is the first and second top health concern across all age groups in 2019, per HealthFocus. Nearly one-third look to improve brain function through foods/drinks, per IFIC.
Immunity supplements are projected to reach $3.6 billion by 2021; one-third of those aged 35-54 took an immunity supplement in 2018, 21% aged 55 and over, and 25% aged 18-24, per CRN. One in five want to boost immunity through foods/drinks, according to IFIC.
One-third of adults aged 45 and over tried to lose weight last year vs. 20% less than age 35, according to Packaged Facts’ 2018 Clean Label and Organic Consumer survey.
Half of adults age 50 and over want more energy to do the things they enjoy. Tiredness/lack of energy is the fifth overall U.S. health concern in 2019, per HealthFocus.
Hair, skin, and nail supplement sales reached $1.0 billion in 2018 and are predicted to reach $1.2 billion by 2021, per NBJ. The microbiome ties closely to skin health.
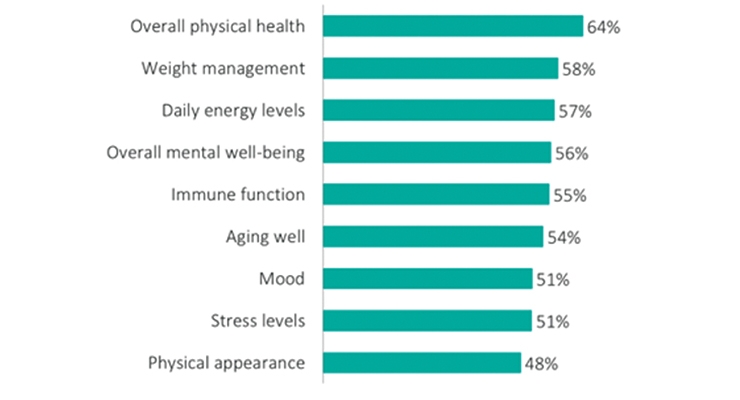
According to Sloan Trend’s TrendSense Predictive Model, the microbiome is a very fast accelerating and very large Level 2 nutraceutical mass market, crossing into the mainstream in 2016 and growing at a torrid pace ever since (Figure 3). Most importantly, medical research activity/studies are also increasing at an exponential rate—solidifying the weight of the scientific evidence regarding the microbiome’s role in health and identifying additional linkages.
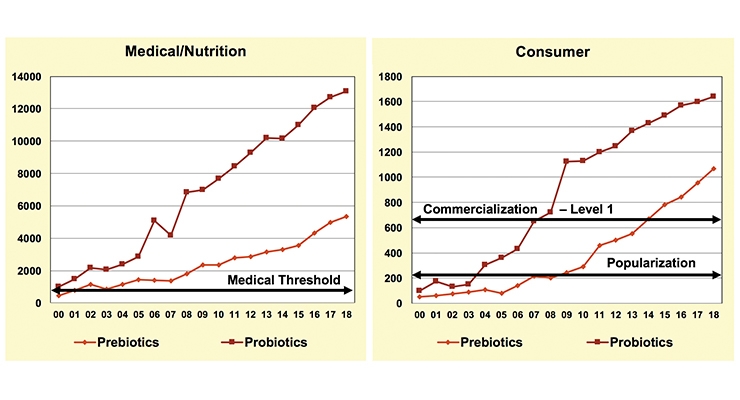
While TrendSense also chronicles explosive growth in medical research activity and in the consumer marketplace for both probiotics and prebiotics, growth in probiotics appears to be maturing/stabilizing as a large Level 1 mass market, while prebiotics—although a smaller market at this point—continues to accelerate (Figure 4).
Figure 3
Source: Sloan Trends Inc., 2019
Figure 4
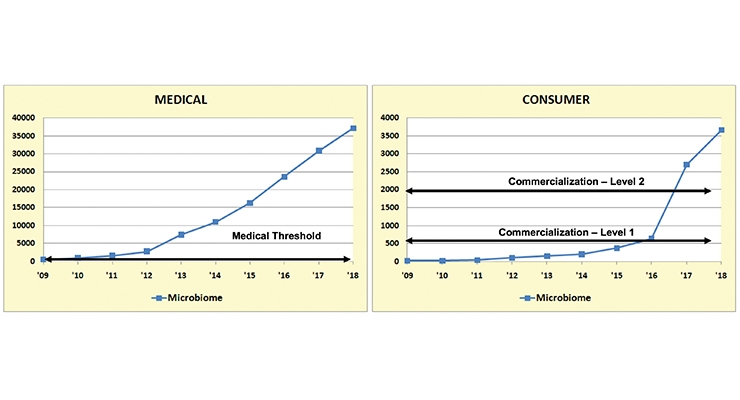
Source: Sloan Trends Inc., 2019
Prebiotics to Rival Probiotics
One out of two consumers associate prebiotics with a healthy digestive system, according to Insights Consulting; 29% of U.S. adults already link prebiotics with healthy digestion and the microbiome.
According to Ooyen Research’s 2018 Ingredient Comparative Survey for the Global Prebiotic’s Association, only about 5% of global supplement users take prebiotics.
Gut health/digestion, followed by regularity, a complement to probiotics, immunity, fiber, brain health/mental acuity, inflammation, and heart health are the health benefits global consumers most associate with prebiotics. Most users look for a prebiotic/probiotic combination.
NBJ projected sales of prebiotic supplements will grow from $96 million to $399 million by 2020; symbiotic supplements from $658 million to $881 million by 2020, with annual growth of 16%. Silk Prebiotics Almond & Cashew is among the new prebiotic milks in the U.S.
Interest in dietary fiber will also accelerate as awareness and understating of prebiotics increase. In June 2018, FDA released a final definition of fiber that included inulin and inulin type fructans, high amylose starch 2, and galactooligosaccharides as prebiotic fibers.
Nearly two-thirds (63%) are trying to get more fiber in their diet, still the most sought-after nutritional ingredient, per Hartman. Boomers and matures are most likely to look for a fiber claim on food/drinks, per FMI’s 2018 U.S. Grocery Shopper Trends.
Children are another yet untapped market for digestive health. One in three grammar school children in the U.S. are sent home from school due to stomach issues ever year, per the National Institute for Diabetes and Kidney and Digestive Diseases. Kids are most likely to suffer from constipation.
Pet foods are another fast-emerging market for digestive health. During the year ended March 2018, Nielsen charted 139% growth in pet products that include prebiotics and probiotics. In 2018, pet product sales containing prebiotics and probiotics increased 24%, per Packaged Facts’ 2019 Pet Market Outlook.
Asia Set Global Pace
Globally, Asia-Pacific is the top market for new gut product launches, led by China, India, and Vietnam, per Mintel’s Gut Health is Today’s Hot Health Issue 2019 Report. The U.S. is the leading country for gut health claims, with 12% of all claims globally.
According to Google Search, consumers worldwide are increasing their online searches for information on the microbiome, and on prebiotics and probiotics as well (Figure 5).
Figure 5
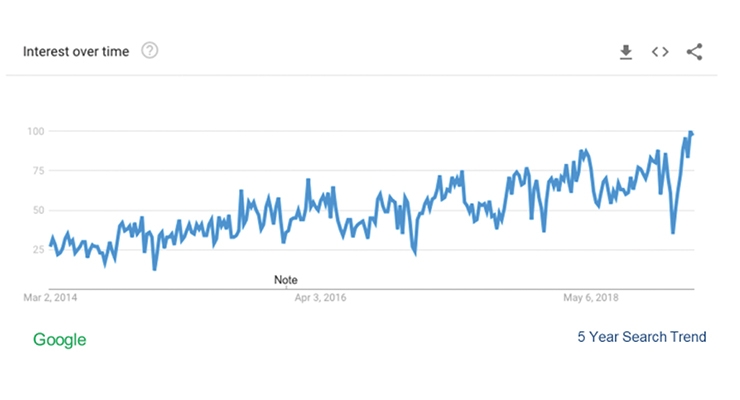
Souce: Google, April 2019
Mintel reported that 44% of Chinese adult supplement users bought probiotic supplements in 2018, 27% of supplement users in India, and 21% in Brazil.
In China, 37% of parents are interested in food/drink with a high fiber claim, 54% of Indian urbanites, and 23% in Italy, per Mintel’s 2019 report.
Although carbohydrate fiber-based prebiotics are most common, the door is open to novel non-fiber based prebiotics that prove capable of supporting beneficial bacteria in the gut and promote a healthy microbiome.
Dr. A. Elizabeth Sloan and Dr. Catherine Adams Hutt are president and chief scientific and regulatory officer, respectively, of Sloan Trends, Inc., Escondido, CA, a 20-year-old consulting firm that offers trend interpretation/predictions; identifies emerging high potential opportunities; and provides strategic counsel on issues and regulatory claims guidance for food/beverage, supplement and pharmaceutical marketers. For more information: E-mail: lizsloan@sloantrend.com; Website: www.sloantrend.com.
Gastrointestinal supplement sales reached $2.96 billion in 2018 and are projected by Nutrition Business Journal (NBJ) to reach $3.98 billion by 2021.
One in five U.S. supplement users took a digestive supplement in 2018; probiotics were the 8th most often used supplement, taken by 17% of all users. One in five (20%) young adults aged 18-34 used a fiber supplement, 16% a probiotic, 7% digestive enzymes, and 5% prebiotics, per CRN’s 2018 Consumer Survey on Dietary Supplements.
Over one-quarter (28%) of adults cite digestive health among the top three benefits they want from foods/beverages, per IFIC’s 2018 Food & Health Survey; two-thirds of those age 50 and over say digestive health is extremely/very important. Four in 10 adults (43%) are trying to get more probiotics in their diet, per Hartman’s Wellness 2017.
OTC digestive remedies, including antacids, laxatives, anti-gas, and anti-diarrhea reached $4.9 billion in 2018, up 11.9% over the past five years, per Mintel.
Yet it’s the mounting medical evidence, and growing consumer awareness, that a healthy gut microbiome can deliver a wealth of high-demand and often difficult-to-achieve health benefits, (e.g., improved mood and better memory) that is poised to drive explosive growth in the digestive market—and the timing is now!
Microbiome Moves Center Stage
According to HealthFocus’ 2019 U.S. Consumer Trends Survey, over one-third (37%) of U.S. consumers are aware of and extremely/very interested in the gut microbiome, and how good and bad bacteria in the gut impact overall health. Young adults aged 18-39 and those in households with kids are most interested.
Two-thirds of those who take a probiotic supplement do so for a healthier microbiome/gut, 49% general well-being, 45% regularity, 43% immunity, 34% to replenish good bacteria after antibiotic use, and 32% for better nutrient absorption, per Mintel’s February 2019 Gut Health is Today’s Hot Health Issue report (Figure 1).
Figure 1

Source: Mintel, 2019
Most important, 64% of consumers believe their digestive health plays an extremely/very important role in their physical health, 58% weight management, 57% daily energy levels, 56% overall mental well-being, 55% immune function, 54% aging well, 51% mood/stress levels, and 48% physical appearance, per HealthFocus (Figure 2).
A significant body of scientific evidence supports a connection via the gut-brain axis for improved cognitive health, mood, reduced stress, and potentially neurodegenerative conditions (e.g., Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease).
In a 2017 NBJ survey, nutraceutical manufacturers cited brain health as the top opportunity for the next few years. In 2018, CRN reported that 26% of users bought a supplement for mental/brain health. Brain/cognitive supplements sales are projected to exceed $1 billion by 2021, per NBJ; mental health/mood and anti-stress supplements reached $706 million in 2018.
Figure 2

Source: HealthFocus, 2019
Maintaining brain function with age is the first and second top health concern across all age groups in 2019, per HealthFocus. Nearly one-third look to improve brain function through foods/drinks, per IFIC.
Immunity supplements are projected to reach $3.6 billion by 2021; one-third of those aged 35-54 took an immunity supplement in 2018, 21% aged 55 and over, and 25% aged 18-24, per CRN. One in five want to boost immunity through foods/drinks, according to IFIC.
One-third of adults aged 45 and over tried to lose weight last year vs. 20% less than age 35, according to Packaged Facts’ 2018 Clean Label and Organic Consumer survey.
Half of adults age 50 and over want more energy to do the things they enjoy. Tiredness/lack of energy is the fifth overall U.S. health concern in 2019, per HealthFocus.
Hair, skin, and nail supplement sales reached $1.0 billion in 2018 and are predicted to reach $1.2 billion by 2021, per NBJ. The microbiome ties closely to skin health.
According to Sloan Trend’s TrendSense Predictive Model, the microbiome is a very fast accelerating and very large Level 2 nutraceutical mass market, crossing into the mainstream in 2016 and growing at a torrid pace ever since (Figure 3). Most importantly, medical research activity/studies are also increasing at an exponential rate—solidifying the weight of the scientific evidence regarding the microbiome’s role in health and identifying additional linkages.
While TrendSense also chronicles explosive growth in medical research activity and in the consumer marketplace for both probiotics and prebiotics, growth in probiotics appears to be maturing/stabilizing as a large Level 1 mass market, while prebiotics—although a smaller market at this point—continues to accelerate (Figure 4).
Figure 3

Source: Sloan Trends Inc., 2019
Figure 4

Source: Sloan Trends Inc., 2019
Prebiotics to Rival Probiotics
One out of two consumers associate prebiotics with a healthy digestive system, according to Insights Consulting; 29% of U.S. adults already link prebiotics with healthy digestion and the microbiome.
According to Ooyen Research’s 2018 Ingredient Comparative Survey for the Global Prebiotic’s Association, only about 5% of global supplement users take prebiotics.
Gut health/digestion, followed by regularity, a complement to probiotics, immunity, fiber, brain health/mental acuity, inflammation, and heart health are the health benefits global consumers most associate with prebiotics. Most users look for a prebiotic/probiotic combination.
NBJ projected sales of prebiotic supplements will grow from $96 million to $399 million by 2020; symbiotic supplements from $658 million to $881 million by 2020, with annual growth of 16%. Silk Prebiotics Almond & Cashew is among the new prebiotic milks in the U.S.
Interest in dietary fiber will also accelerate as awareness and understating of prebiotics increase. In June 2018, FDA released a final definition of fiber that included inulin and inulin type fructans, high amylose starch 2, and galactooligosaccharides as prebiotic fibers.
Nearly two-thirds (63%) are trying to get more fiber in their diet, still the most sought-after nutritional ingredient, per Hartman. Boomers and matures are most likely to look for a fiber claim on food/drinks, per FMI’s 2018 U.S. Grocery Shopper Trends.
Children are another yet untapped market for digestive health. One in three grammar school children in the U.S. are sent home from school due to stomach issues ever year, per the National Institute for Diabetes and Kidney and Digestive Diseases. Kids are most likely to suffer from constipation.
Pet foods are another fast-emerging market for digestive health. During the year ended March 2018, Nielsen charted 139% growth in pet products that include prebiotics and probiotics. In 2018, pet product sales containing prebiotics and probiotics increased 24%, per Packaged Facts’ 2019 Pet Market Outlook.
Asia Set Global Pace
Globally, Asia-Pacific is the top market for new gut product launches, led by China, India, and Vietnam, per Mintel’s Gut Health is Today’s Hot Health Issue 2019 Report. The U.S. is the leading country for gut health claims, with 12% of all claims globally.
According to Google Search, consumers worldwide are increasing their online searches for information on the microbiome, and on prebiotics and probiotics as well (Figure 5).
Figure 5

Souce: Google, April 2019
Mintel reported that 44% of Chinese adult supplement users bought probiotic supplements in 2018, 27% of supplement users in India, and 21% in Brazil.
In China, 37% of parents are interested in food/drink with a high fiber claim, 54% of Indian urbanites, and 23% in Italy, per Mintel’s 2019 report.
Although carbohydrate fiber-based prebiotics are most common, the door is open to novel non-fiber based prebiotics that prove capable of supporting beneficial bacteria in the gut and promote a healthy microbiome.
Dr. A. Elizabeth Sloan and Dr. Catherine Adams Hutt are president and chief scientific and regulatory officer, respectively, of Sloan Trends, Inc., Escondido, CA, a 20-year-old consulting firm that offers trend interpretation/predictions; identifies emerging high potential opportunities; and provides strategic counsel on issues and regulatory claims guidance for food/beverage, supplement and pharmaceutical marketers. For more information: E-mail: lizsloan@sloantrend.com; Website: www.sloantrend.com.