Exclusives
Minding Mental Health with Nutraceuticals: Global Opportunities
The mammoth, mufti-faceted mental health market is poised to be the next explosive health platform.

By: Sean Moloughney
Just over one-quarter of global consumers surveyed by Ipsos’ Global Health Monitor Service (27 markets, November 2020) cited mental health among the top health issues affecting their country, just behind coronavirus and cancer, and ahead of stress and obesity. Those living in Sweden followed by Chile, Australia, Great Britain, Canada, Peru, and the U.S. were most likely to say so.
After diabetes and heart disease, mental health is the health issue global consumers are extremely concerned about for the future, per Euromonitor’s 2021 Voice of the Consumer: Health and Wellness Survey.
Mental well-being, followed by a healthy immune system, feeling good, getting enough sleep, the absence of disease, and emotional well-being, are now the top criteria by which global consumers define “being healthy,” according to Euromonitor’s 2021 survey.
Recent news coverage, including Prince William’s and Harry’s public discussions of their mental health struggles since their mother’s death and the pressures/emotional issues affecting this year’s Olympic gymnasts, have helped to remove the stigma of publicly discussing mental health matters.
Sadly, the ebb and flow of COVID-19 will continue to impact global mental health for the foreseeable future. The coronavirus still remains consumers’ greatest worry worldwide, followed by unemployment, per Ipsos’ August 2021 What Worries the World?
Only one-third of consumers expect to return to something close to their pre-pandemic lifestyle in the next year, per Ipsos’ April 2021 survey for the World Economic Forum (30 countries). One-third of Japanese consumers and one-quarter of those in France and Australia believe COVID-19 will never be contained.
Although those living in China and Saudi Arabia say their country’s economy has recovered from the pandemic, the majority in the other 27 countries surveyed by Ipsos expect recovery will take at least two years (Local Economic Recovery from Covid-19, August 2021).
As the Delta variant spreads, Ipsos’ September Global Consumer Confidence Index plateaued at a level similar to March 2020, and below January 2020 when COVID began to spread across the globe. Inflation and unemployment will remain ongoing stressors. Multi-functional, value-based health products will remain in high demand.
Four in 10 global consumers say that COVID will have a long-lasting negative effect on mental health, per Ipsos’ Global Perceptions of the Impact of COVID (2021).
Most important, with major market research firms reporting pockets of improved mental health in the past year, the number of people trying to manage/treat mental health issues remains at levels similar to pre-pandemic years. Although very high, and with new mental health markets/needs emerging, a deeper understanding of consumers’ shifting mental health priorities, concerns, and the modalities of choice best suited for supplements and functional foods is essential.
Globally Speaking
According to Innova Market Insights’ 2021 global survey of 10 countries, half (53%) of consumers say they’ve taken action to improve their physical health; 44% their mental/emotional health; and one-third their spiritual health in the past year.
More consumers from six major countries—surveyed in the Hartman Group’s July 2021 Health & Wellness Across the Globe—reported more improvements than declines to their overall and mental health in the past year, with the exception of Germany (Figure 1). One-quarter report mental improvements in 2021, per Ipsos’ global perceptions survey.
Figure 1. Change in Mental Health During the Past Year
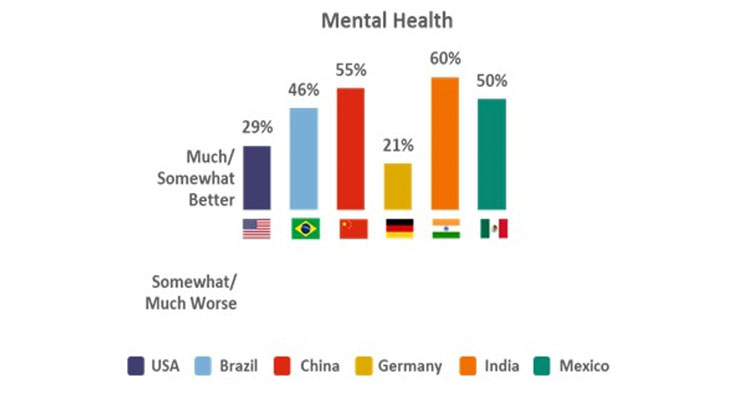
Source: Hartman Group’s Health & Wellness Across the Globe Report
Stress ranked third among the health concerns consumers in China, the U.K., Germany, Spain, Brazil, and the U.S. were extremely/very concerned about in Q4 2020, per HealthFocus Beyond COVID-19 survey. Lack of energy/tiredness was fourth, sleep problems sixth, lack of mental sharpness/focus seventh, and anxiety eighth—all cited by more than half of those surveyed
(READ MORE: Post COVID-19: A New World of Health & Nutrition Opportunities.)
In Euromonitor’s 2021 survey, over half (57%) of global consumers still report at least moderate levels of stress—51% anxiety. Those living in Japan, followed by India, Italy, France, the U.S., and South Korea were most likely to report high/extreme levels of stress. One-third of global consumers are taking measures to manage stress/anxiety.
Lack of mental sharpness was the eighth health concern in China, and sixth in the U.K., in Q4 2020, per HealthFocus; depression was sixth in Germany.
Those aged 65 and older are most concerned about memory and retaining mental sharpness with age, per HealthFocus. In descending order, Japan, Italy, Finland, Portugal, Greece, and Germany have the highest percentage of seniors in their population, per World bank data. China, India, the U.S., Japan, and Russia have the largest absolute number of those aged 65 and older.
In Q4, sleep problems were second only to COVID-19 in China as a health concern, eighth in Germany, and ninth in the U.K., per HealthFocus. Products that provide health benefits and help you sleep (e.g., restoring nutrients, building immunity, muscle, bone, or lowering cholesterol) will be in high demand. Brands may consider pairing sleep aids for post-menopausal women, who medically most often suffer from insomnia.
Long-lasting energy was the fourth reason global consumers (20%) recently bought a functional food/drink, per Innova (July 2021). Half (53%) of global consumers say they always/usually choose foods/drinks for increased energy; 61% aged 18-29, per HealthFocus. Lack of energy/tiredness was the second health concern after COVID in Germany, fourth in the U.K., and seventh in China, per HealthFocus.
The incidence of happiness has declined by eight points or more in Peru, Chile, Mexico, India, the U.S., Australia, Canada, and Spain in the past year, while increasing significantly in China, Russia, Malaysia, and Argentina per Ipsos’ Global Happiness (October 2020).
Over half (55%) of global consumers say their health/physical well-being is their greatest source of happiness. Feeling good about oneself ranks among the most important aspects of health/wellness in the U.S., Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico but not in China, per Hartman. Unilever’s Olly now offers a Hello Happy Supplement.
State Side
Eight in 10 Americans now say that good mental/emotional health and getting enough sleep are important contributors to overall health, more so than exercise (55%), per HealthFocus (2021 USA Trend Study).
Retaining mental sharpness as they age is second only to COVID-19 among the health concerns Americans are extremely/very concerned about in 2021; memory ranks fifth, stress eighth, tiredness/lack of energy ninth, and lack of mental sharpness/focus fourteenth, according to HealthFocus (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Top Health Concerns (Extremely/Very Concerned About)
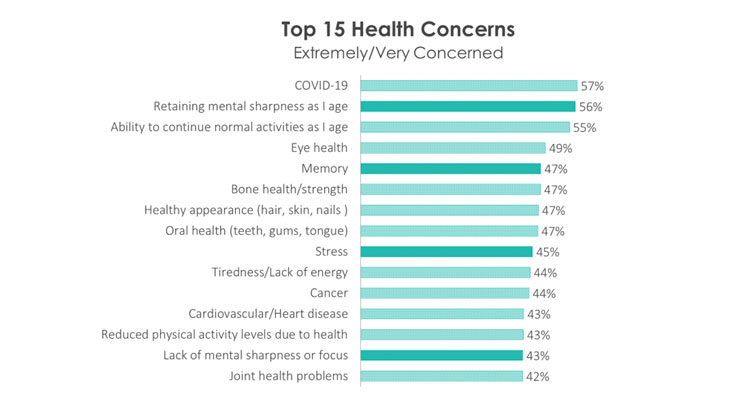
Source: HealthFocus International 2021 USA Trend Study
Concerns continue to differ significantly by age. Maintaining mental sharpness with age, memory, and lack of mental sharpness/focus are significantly more important to those aged 65 and older in the U.S.; stress, anxiety, mood and depression to younger adults.
Mood swings and irritability are a fast-emerging issue for those aged 18-29, per HealthFocus. A Nutrition Business Journal (NBJ) 2021 survey (Q2) reports mood remains a “state-of-mind” condition for half of Gen Zers/Millennials and four in 10 Gen Xers, as does stress.
Gen Z, Millennial, and Gen X consumers are most likely to say the pandemic has affected their ability to get a good night’s sleep and that they’re not as focused or able to concentrate on tasks as before, per the Natural Marketing Institute’s COVID-19 2020 Survey.
After being a borderline and lackluster very low-level mass market opportunity from 2009-2016—but a viable market in nutrition specialty/health food channels—mood in the context of nutraceuticals has accelerated and is approaching a highly desirable Level 3 mass market, according to Sloan Trend’s TrendSense model (Figure 3). Mood is supported by a large but relatively slowly accelerating level of medical research activity critical for generating new findings and solidifying scientific support. While it is yet to be seen if mood will mature into a high Level 2 or Low Level 3 market, it is a viable cutting-edge nutraceutical product opportunity at this time.
Figure 3. TrendSense Predictive Model: Mood
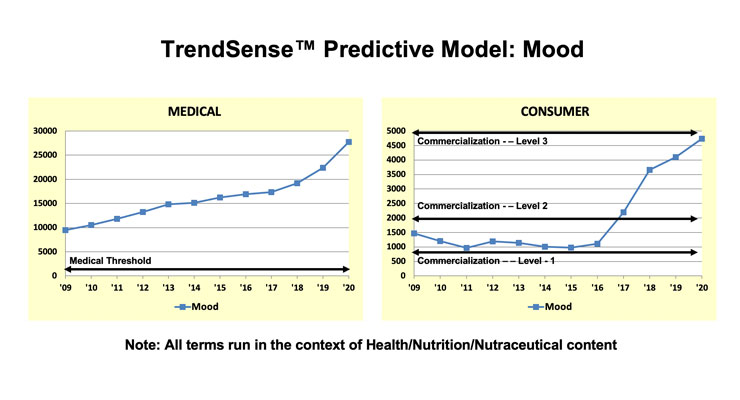
Source: Sloan Trends, Inc. 2021
One-quarter of U.S. consumers would like more mental energy from foods/drinks, per HealthFocus; one in five more energy to jump start the morning.
Four in 10 U.S. adults link protein with improved mental energy and brain nourishment, per HealthFocus. As of Q2, NBJ reports energy levels are top-of-mind for four in 10 Gen Zers/Millennials; one-third of Gen Xers.
Maintaining focus/concentration on schoolwork is cited by four in 10 parents as the biggest issue affecting children globally post-pandemic, according to Ipsos’ July 2021 World Youth Skills Survey. Pre-pandemic, half of global moms were already very/extremely concerned about their child’s mental/intellectual development, per HealthFocus.
Over half of American moms cite depression, stress, and anxiety among their top health worries for their kids. Over-one third have noticed anxiety, 31% depression, and 24% sleep in their teenage girls; one in five, respectively, in their teenage boys, per Mott Children’s Hospital 2021 National Poll on Children’s’ Health.
Innova reports that 17% of all global new food/beverage launches with functional ingredients were for babies/toddlers in 2020, second only to sports nutrition launches. Global infant formula sales are projected to reach $92 billion by 2024, according to MarketsandMarkets.
Lastly, demand for immune boosting and stress/anxiety-reducing benefits drove U.S. pet supplement sales up 21% in 2020 to nearly $800 million, quadrupling the 2019 growth rate, per Packaged Facts 2020 Pet Supplements: U.S. Pet CBD supplement sales approached $100 million last year; one-quarter of dog owners bought a stress/anxiety/calm supplement; 24% of cat owners.
Mindful Modalities
Half (53%) of consumers are treating or trying to prevent anxiety or stress in their household; 44% depression, according to the Hartman Group’s July Health & Wellness 2021: Reimagining Well-Being Amid COVID-19 report (Figure 4).
Figure 4. Conditions Treating and/or Preventing in Household (2021)
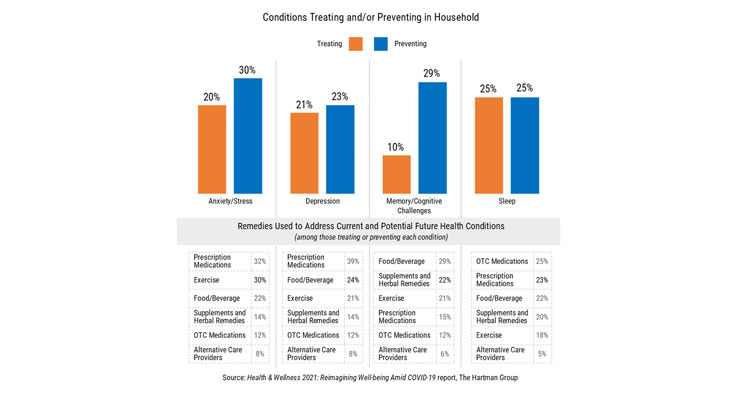
Source: The Hartman Group (Health & Wellness 2021: Reimagining Well-Being Amid COVID-19)
Most important, despite high rates of reported symptoms/worries, those that self-report treating or managing stress, anxiety, or depression in their household remains relatively consistent with levels from the prior year, including pre-pandemic.
Rx medication remains the top choice for managing/treating anxiety/stress and depression; food/beverage followed by supplements for memory/cognition; and OTC medication for sleep, per Hartman (Figure 4).
After health, improved mental well-being is the most important motivator for the 66% who exercise regularly; mental acuity ranks fourth, per IHRSA’s 2021 The Next Fitness Consumer. Half of those who have returned to the gym did so to boost their mood, energy level, and/or to reduce stress.
Of the two-thirds of global consumers (67%) who exercise strenuously or moderately at least three times per week, four in 10 do so to improve mood; half of exercisers aged 18-29, per HealthFocus.
“Exercise as Medicine,” where exercise is used to treat health issues, is the third “hot” fitness trend for 2021 in Europe and Asia, eighth in the U.S. and fourteenth in China, according to the American Academy of Sports Medicine’s 2021 Worldwide Survey of Fitness Trends.
Functional Foods
Global sales of fortified/functional beverages reached $102 billion in 2020; sales of fortified/functional foods reached $173 billion, per Euromonitor.
According to Kerry’s June 2021 Global Survey (16 countries), 42% of global consumers bought more functional foods/drinks since the pandemic began. New functional food/drink launches have increased 59% from 2016 through 2020, per Innova.
Energy is the second health benefit U.S. consumers most want to get from foods/drinks; sleep is sixth, brain focus (memory, cognition, focus) ninth, and emotional/mental health eleventh, per IFIC Food & Health Survey, 2021.
Dietary Supplements
In the U.S., sales of mood and mental health supplements reached $1.2 billion in 2020, up 29.4%, and are projected to grow 10-12% through 2024, per NBJ’s 2021 Condition Specific Report (Figure 5).
Brain/cognitive supplement sales topped $1 billion and are projected to reach $1.3 billion by 2023, per NBJ (June 2021).
According to CRN’s 2020 U.S. Dietary Supplement Survey, 13% of supplement users took supplements for mental health support; led by those aged 18-34 (21%). Melatonin (37%), magnesium (31%), CBD (16%), theanine (14%), and St. John’s Wort (12%) were among the top products consumers reported taking.
Similarly, 14% of supplement users took a supplement for sleep. Two-thirds took melatonin, 28% magnesium, 19% lavender, 19% valerian, 17% CBD, and 10% Ginkgo biloba.
Amino acids supplements are enjoying year-on-year growth of 34%, per NBJ. Tryptophan and L-theanine are moving into the functional food spotlight.
Hemp CBD products (e.g., supplements, topicals, foods/beverage, and pet products) declined 2.4% to $803 million, per NBJ. Non-dispensary hemp/CBD beverages reached nearly $200 million in sales, according to BDSA/IRI for the year ended July 2021.
Globally, 69% believe the microbiome/good digestive health is extremely/very important for overall mental health, daily energy 66%, mood 65%, and stress levels 63%, per HealthFocus. Over half (57%) of U.S. consumers link the microbiome to daily energy levels, 56% overall mental well-being, 51% mood, and 51% stress levels.
Herbs/botanicals were the second fastest growing supplement category in 2020, per NBJ. Combination herbals accounted for 15% of mood/mental health supplement sales, hemp/CBD 14%.
According to Kerry’s 2021 Botanical State of Mind global survey (12 countries, 6,500 consumers), honeysuckle, rosehip, and lavender are most associated with the emotion of caring; cherry blossom, elderflower, jasmine, and vanilla with peaceful; guarana, ginseng, kola nut, and ginger with energy; and fenugreek, honeysuckle, and hibiscus with being friendly.
One-third (36%) of global consumers believe botanicals are beneficial for sleep, 35% for stress, 34% for cognitive/brain health, and 33% for mood management, per Kerry.
The Science of the Gut-Brain Axis
There is clear and convincing evidence of a link between gut physiology and brain function. The link is bi-directional and involves neural pathways that include neuroendocrine signaling, immune activation and signaling, altered intestinal permeability, modulation of enteric sensory-motor reflexes, and enteroendocrine signaling.
The gut microbiota may influence stress-related behaviors, including anxiety and depression. This link is believed to be primarily through immune system functions, since the gut-associated lymphoid tissue is the largest immune organ in the human body, accounting for more than 70% of the total immune system.
The key mechanism for stress and anxiety management through the gut may be through modulation of the immune system and control of inflammation. Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species have been studied in multiple clinical trials with mixed results.
Based on clinical evidence, specific probiotic strains and their combinations (symbiotics) may be effective. For stress, B. lactis BB12, L. casei, L. acidophilus, L. rhamnosus, L. bulgaricus, B. breve, B. longum (all at 1 x 107 CFU/g) with Streptococcus thermophiles (2.9 x 1010 CFU/g) have shown positive results (Mohammadi AA et al (2016) Nutr Neurosci 19:387-395).
For anxiety, L. Paracasei ssp paracasei F19 L. acidophilus La5, and B. lactis BB12 (all at 5 x 107 CFU/g) have been studied with positive outcomes (Simren M et al (2010) Aliment Pharmacol Ther 31:218-227).
L. plantarum P8 (2 g/d) (1 x 1010 CFU/g) has been shown to be effective for managing stress and anxiety (Lew LC (2019) Clin Nutr 38:2053-2064). L. casei Shirota 9029 (1 x 109 CFU/g) has supported sleep in clinical trials (Takeada M et al (2017) Benef Microbes 8:153-162). Probiotics have not shown significant effects on cortisol levels.
Other ingredients that may support mood and manage stress/anxiety through inflammation control include turmeric, astaxanthin, ginger, and green tea. Mushrooms, including Maitake, Shiitake, and Turkey tail may also support immune function. Adaptogens, including ashwagandha, and the Reishi mushroom may also offer mood and stress support.
Disturbances to the microbial balance in early life may promote a chronic inflammatory state that can lead to adverse changes in mood and behavior, including increased responsiveness to stress and incidence of stress-related disorders.
Dr. A. Elizabeth Sloan and Dr. Catherine Adams Hutt are president and chief scientific and regulatory officer, respectively, of Sloan Trends, Inc., Escondido, CA, a 20-year-old consulting firm that offers trend interpretation/predictions; identifies emerging high potential opportunities; and provides strategic counsel on issues and regulatory claims guidance for food/beverage, supplement and pharmaceutical marketers. For more information: E-mail: lizsloan@sloantrend.com; Website: www.sloantrend.com.