10.20.17
The latest results from an annual survey on dietary supplements revealed an all-time high for supplement usage among U.S. adults, with 76% reporting they consume dietary supplements, up five percentage points from last year’s results. The new survey, 2017 CRN Consumer Survey on Dietary Supplements, was commissioned by the Council for Responsible Nutrition (CRN) and conducted by Ipsos Public Affairs. The survey also found that nearly nine in ten (87%) U.S. adults have confidence in the safety, quality, and effectiveness of dietary supplements overall. Additionally, 76% of U.S. adults perceive the dietary supplement industry as trustworthy, up three percentage points from last year.
“These findings reinforce the upward trend in usage and confidence seen last year,” said Nancy Weindruch, vice president, communications, CRN. “Seeing more than three quarters of Americans taking supplements is an indicator of our industry’s success in bringing products to the marketplace that are valued by the majority of Americans for their role in health and wellness.”
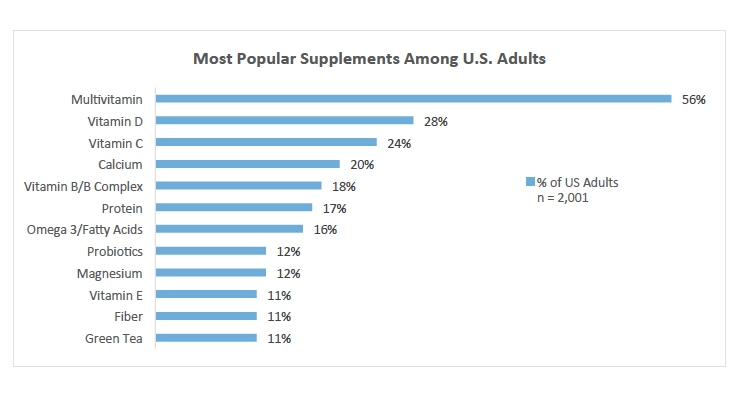
In terms of the types of supplements being taken, the survey found that vitamins/minerals are the most commonly consumed supplement category, consistent with the previous surveys, with 75% of U.S. adults saying they have taken these in the past twelve months. The second most popular category is specialty supplements (38%), followed by herbals/botanicals (29%), sports nutrition supplements (22%), and weight management supplements (15%).
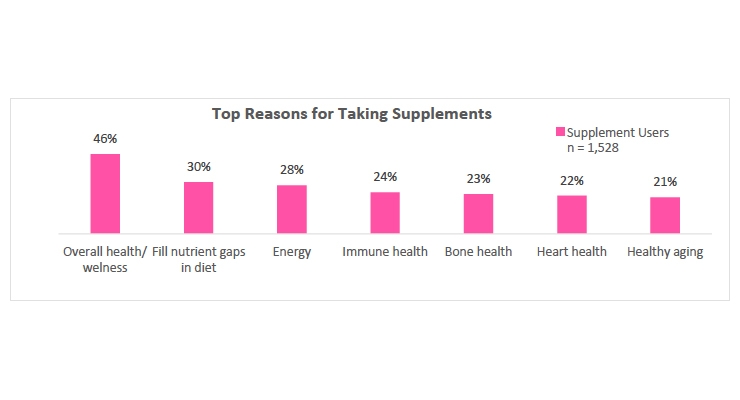
Overall health/wellness benefits is the main reason cited by supplement users for taking dietary supplements (46%). Three in ten (30%) consume supplements to fill nutrient gaps in their diet and similar proportions (28%) use them for energy. Of those who do not take dietary supplements, nearly half (45%) say they might consider taking supplements in the future if a doctor recommended it to them.
In its eighteenth consecutive year, the CRN Consumer Survey on Dietary Supplements serves as the leading resource for statistics on usage of and confidence in dietary supplements. The survey was conducted Aug. 24–28 by Ipsos Public Affairs and was funded by CRN. The survey was conducted online in English and included a national sample of 2,001 adults aged 18 and older living in the United States, including 1,528 among those who are considered supplement users. The survey has been conducted annually since 2000. The precision of Ipsos online polls are measured using a credibility interval. In this case, the poll has a credibility interval of plus or minus 2.5 percentage points for all respondents, and plus or minus 2.9 percentage points for supplement users (see Ipsos’ online polling methodology for more info).
“These findings reinforce the upward trend in usage and confidence seen last year,” said Nancy Weindruch, vice president, communications, CRN. “Seeing more than three quarters of Americans taking supplements is an indicator of our industry’s success in bringing products to the marketplace that are valued by the majority of Americans for their role in health and wellness.”
In terms of the types of supplements being taken, the survey found that vitamins/minerals are the most commonly consumed supplement category, consistent with the previous surveys, with 75% of U.S. adults saying they have taken these in the past twelve months. The second most popular category is specialty supplements (38%), followed by herbals/botanicals (29%), sports nutrition supplements (22%), and weight management supplements (15%).

Overall health/wellness benefits is the main reason cited by supplement users for taking dietary supplements (46%). Three in ten (30%) consume supplements to fill nutrient gaps in their diet and similar proportions (28%) use them for energy. Of those who do not take dietary supplements, nearly half (45%) say they might consider taking supplements in the future if a doctor recommended it to them.

In its eighteenth consecutive year, the CRN Consumer Survey on Dietary Supplements serves as the leading resource for statistics on usage of and confidence in dietary supplements. The survey was conducted Aug. 24–28 by Ipsos Public Affairs and was funded by CRN. The survey was conducted online in English and included a national sample of 2,001 adults aged 18 and older living in the United States, including 1,528 among those who are considered supplement users. The survey has been conducted annually since 2000. The precision of Ipsos online polls are measured using a credibility interval. In this case, the poll has a credibility interval of plus or minus 2.5 percentage points for all respondents, and plus or minus 2.9 percentage points for supplement users (see Ipsos’ online polling methodology for more info).